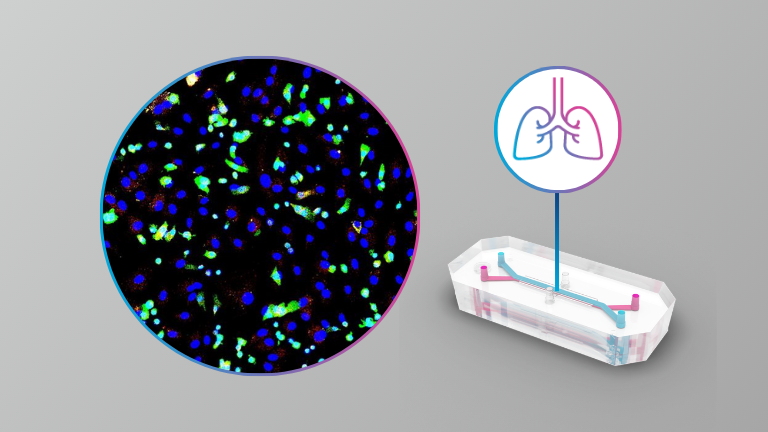
Organ Model: Lung (Airway)
Application: Infectious Disease
Highlights
Researchers used a human Airway Lung-Chip—adjacent channels lined with primary bronchial epithelium (NHBE) and pulmonary microvascular endothelium (HPMEC) under continuous flow—to expose both tissues to the P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing metabolite 2-aminoacetophenone (20 µM, 12 h) and perform RNA-seq to map cell–cell crosstalk. The Airway Lung-Chip provided a human-relevant, dynamic model that uncovered how a single bacterial QS molecule differentially reprograms airway epithelial and endothelial biology, implicating pathways and disease biomarkers that could guide therapeutic targeting.