organ-Chip model
Brain-Chip R1
A first-in-class, isogenic model of the human neurovascular unit

OVERVIEW
5 iPSC-derived cell types, one isogenic system
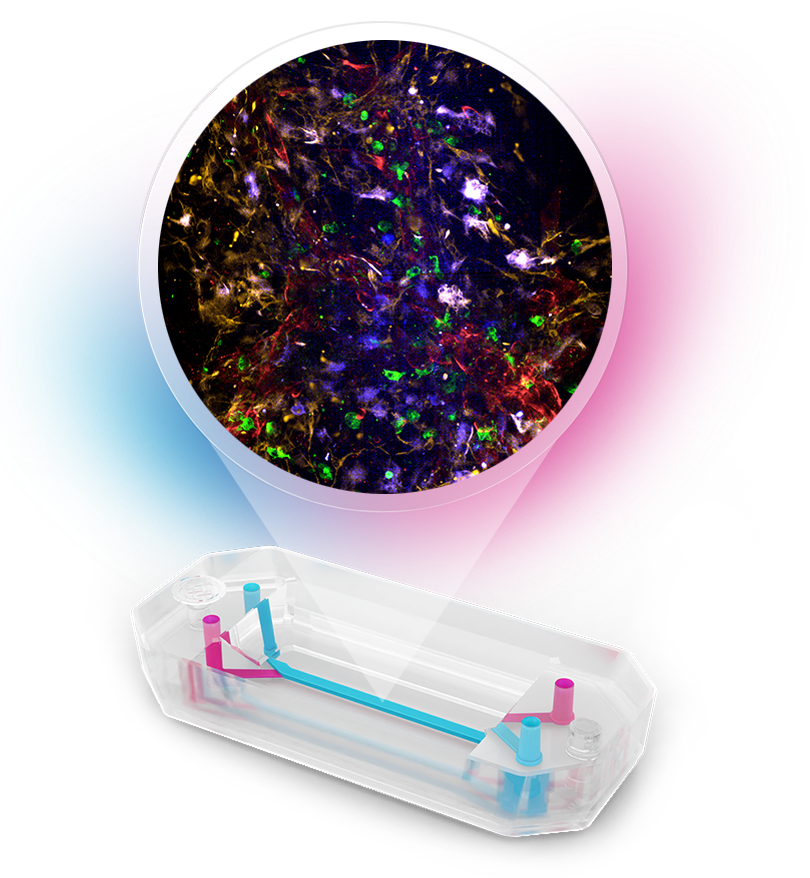
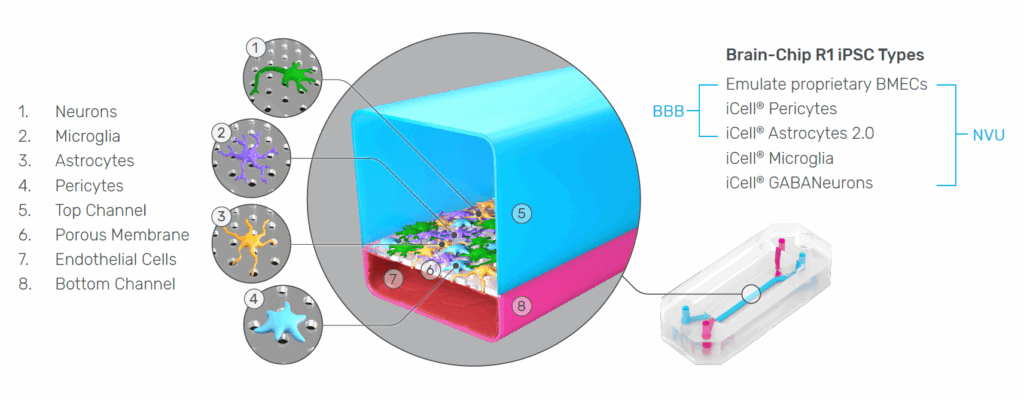
The Brain-Chip R1 is an isogenic, iPSC-derived Organ-Chip model designed to recapitulate the cellular diversity and functional interactions of the human neurovascular unit (NVU). This model integrates five iPSC-derived cell types—neurons, astrocytes, microglia, pericytes, and Emulate’s proprietary brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs)—within a dynamic, perfused microenvironment. These features combine to create a robust, reproducible, and physiologically relevant platform for studying BBB transport and neuroinflammatory mechanisms.
.
KEY BENEFITS
Fully Isogenic NVU Model
Integrates five iPSC-derived cell types from a single donor line to recreate human neurovascular biology with reduced variability and improved reproducibility.
Resting, Physiologically Relevant Sate
Maintains quiescent glia, stable barrier function, and appropriate transporter expression to support more predictive BBB transport and neuroinflammation studies across a four-day experimental window.
Direct-to-Chip, Ready-to-Use Workflow
A simplified iPSC maturation process requires no differentiation or pre-plating steps, enabling consistent, ready-to-run experiments. From start to finish, experiments take just 12 days to complete.
Low-Absorption Platform for BBB Studies
Chip-R1’s minimally absorbing materials improve compound recovery and quantitative permeability measurements, supporting more accurate BBB transport assessments.

Model Overview
The Brain-Chip R1 features two parallel channels separated by a thin, porous membrane. The brain channel (top) contains the neural tissue, including neurons, microglia, astrocytes, and pericytes, while the vascular channel (bottom) contains the BMECs. All cells are derived by direct differentiation from a single donor line and can be seeded directly onto the chip, creating a fully isogenic system that minimizes variability and supports reproducible co-culture of neurovascular cell types.
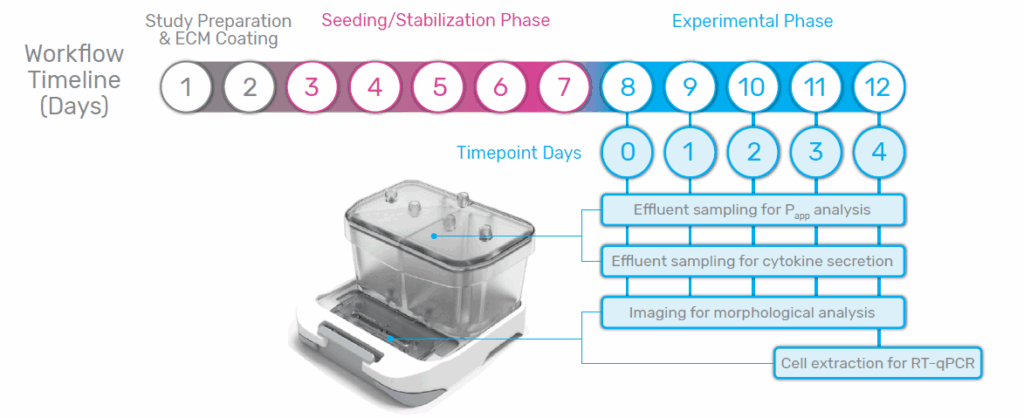
Streamlined Workflow
A Brain-Chip R1 experiment can be completed within a 12-day timeline. Organ-Chip consumables are first prepped for seeding, and then cells are seeded directly onto the chips, connected to flow, and allowed to stabilize before the start of the experimental window. During the experimental phase (Timepoint Days 0-4), daily imaging can be performed to monitor morphology, and effluent can be sampled to analyze barrier integrity and cytokine secretion. At the end of the experimental window, cells can be extracted from the chip for further downstream analysis such as RT-qPCR.
Brain-Chip R1 Characterization
.
BRAIN CHANNEL
Proper Organization of the NVU
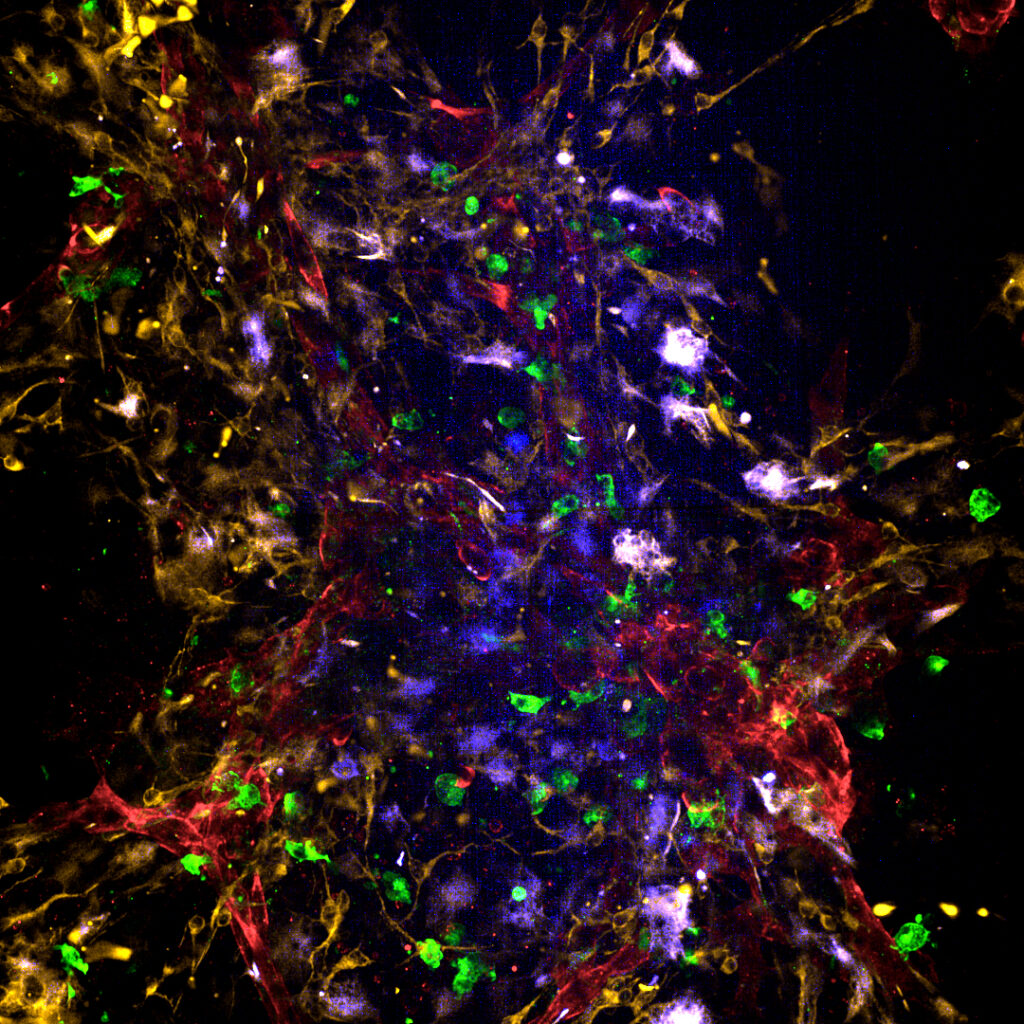
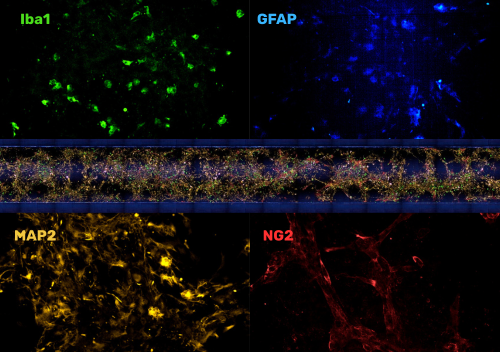
Immunofluorescence imaging of the brain channel reveals that neurons, astrocytes, microglia, and pericytes organize into integrated multicellular clusters with physiologically relevant morphologies. Neurons extend elongated processes, astrocytes display stellate morphologies with branching projections, microglia adopt small ramified forms consistent with a resting state, and pericytes associate closely with neuronal and astrocytic structures. These interactions result in a structurally coherent top channel that visually recapitulates key features of human NVU cytoarchitecture.
.
Vascular Channel
A Physiologically Relevant BBB
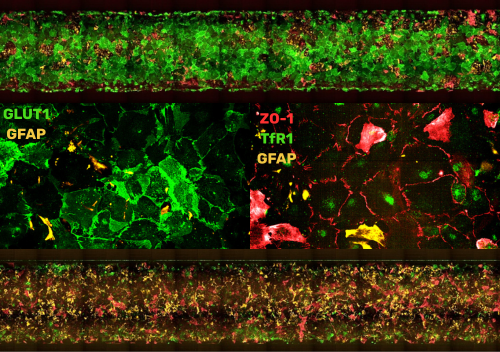
In the vascular channel, BMECs form a confluent endothelial monolayer characterized by continuous ZO-1 staining and expression of canonical tight junction markers. Importantly, these cells exhibit robust expression of BBB-associated transporters—including GLUT1, P-gp, and the transferrin receptor (TfR1). The sustained expression of transporter and tight junction genes, coupled with the absence of epithelial markers such as EPCAM1 and cytokeratins, confirms the BMECs’ endothelial-like identity and distinguishes them from epithelialized models often used in conventional in vitro BBB systems.
.
Inflammatory response
Quiescent Yet Responsive Glia
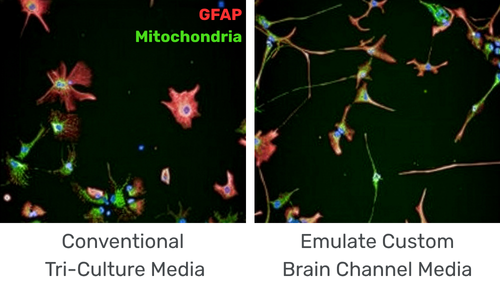
The Brain-Chip R1 maintains glial populations in a physiologically resting state. Baseline cytokine profiling reflects quiescent microglia and astrocytes similar to those found in the healthy CNS. When stimulated with IL-1β, the system mounts a robust, coordinated inflammatory response, demonstrating that the glial populations remain responsive to perturbation and capable of recapitulating neuroinflammatory signaling pathways. Imaging further confirms that optimized channel-specific media preserve resting glial morphologies, whereas alternative media formulations induce signs of activation.
.
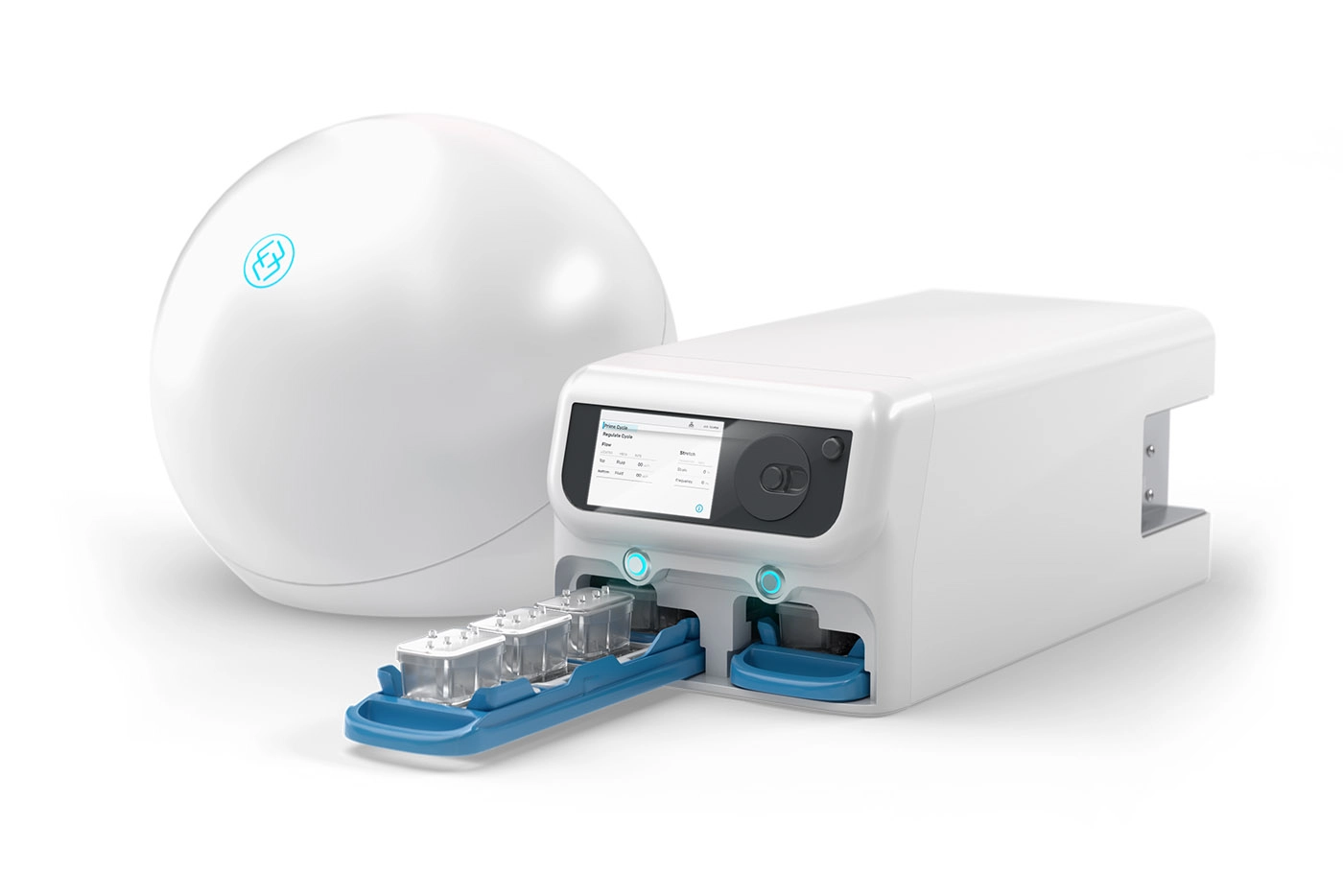
Compatible with Zoë-CM2® Culture Module
The Zoë-CM2 Culture Module is a versatile system for model development & target validation. Capable of culturing up to 12 Organ-Chips at a time, the user-friendly platform gives researchers a window into the inner workings of human biology.

Get Started Today
The Brain-Chip R1 is a BioKit Model that Emulate has internally developed and validated. It is available as a BioKit, which includes pre-qualified cells and media, Organ-Chip consumables, and validated protocols.
Alternately, users can create their own Brain-on-a-Chip model using their own cells sources and a Basic Research Kit.

Learn more
Brain-Chip R1 Webinar
Join us on December 9th for a closer look at Brain-Chip R1! This webinar, presented by Erin Greguske, PhD, and Randy Daughters, PhD, will walk through the development, characterization, and applications of this comprehensive five-cell iPSC model.
.
Speak to an Expert